Iteration node processing workflow
How Iteration Works
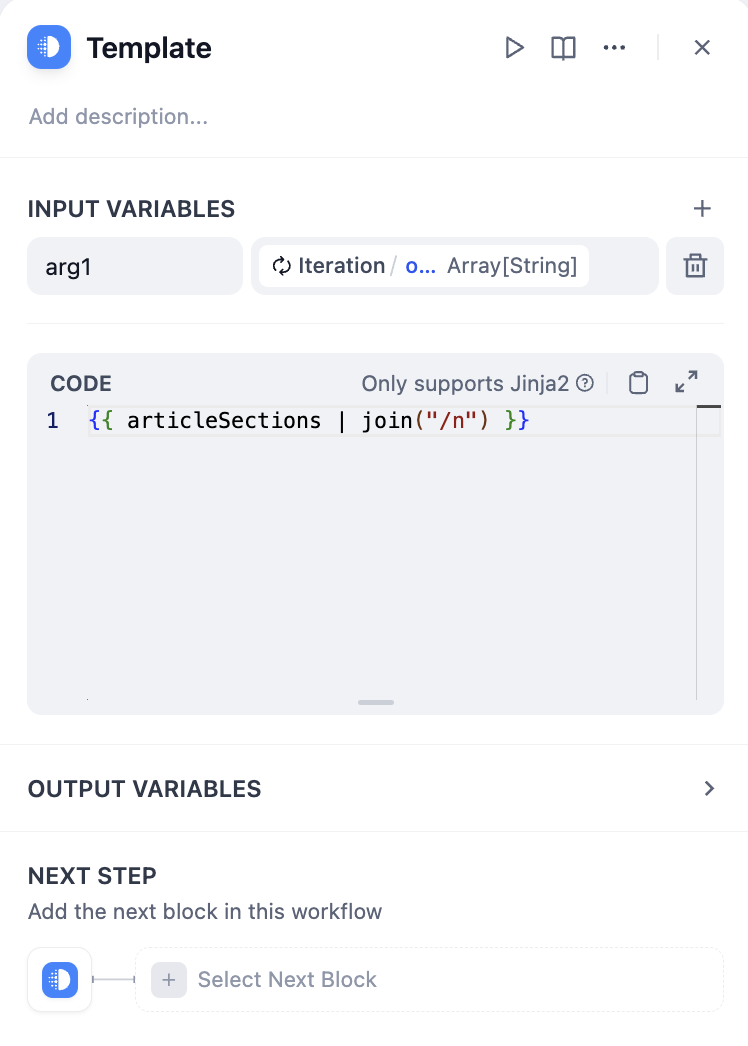
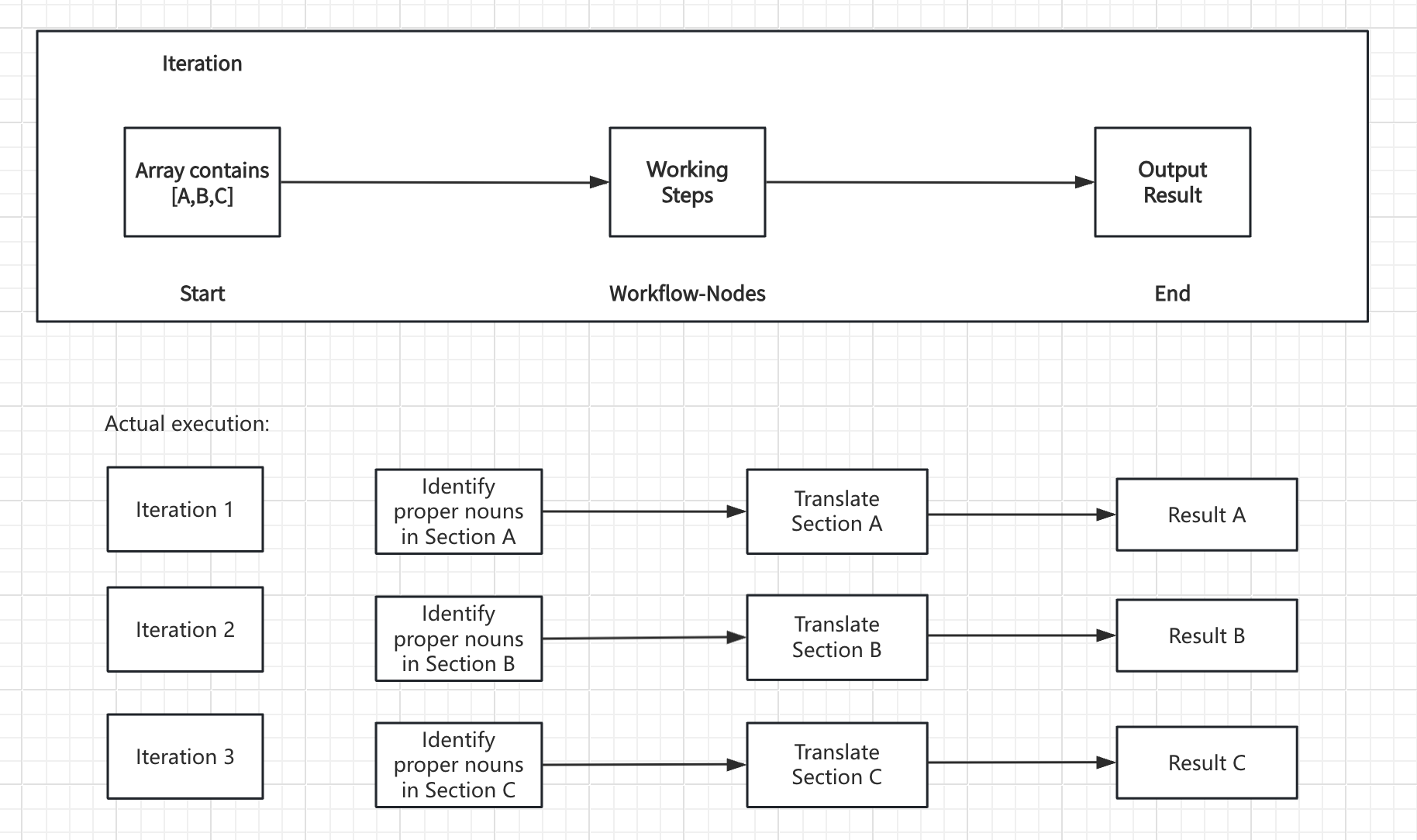
The node takes an array input and creates a sub-workflow that runs once for each array element. During each iteration, the current item and its index are available as variables that internal nodes can reference. Core Components:- Input Variables - Array data from upstream nodes
- Internal Workflow - The processing steps to perform on each element
- Output Variables - Collected results from all iterations (also an array)
Configuration
Array Input
Connect an array variable from upstream nodes such as Parameter Extractor, Code nodes, Knowledge Retrieval, or HTTP Request responses.Built-in Variables
Each iteration provides access to:items[object]- The current array element being processedindex[number]- The current iteration index (starting from 0)
Processing Mode
- Sequential Mode
- Parallel Mode
Sequential Processing - Items processed one after another in orderStreaming Support - Results can be output progressively using Answer nodesResource Management - Lower memory usage, predictable execution orderBest For - When order matters or when using streaming output
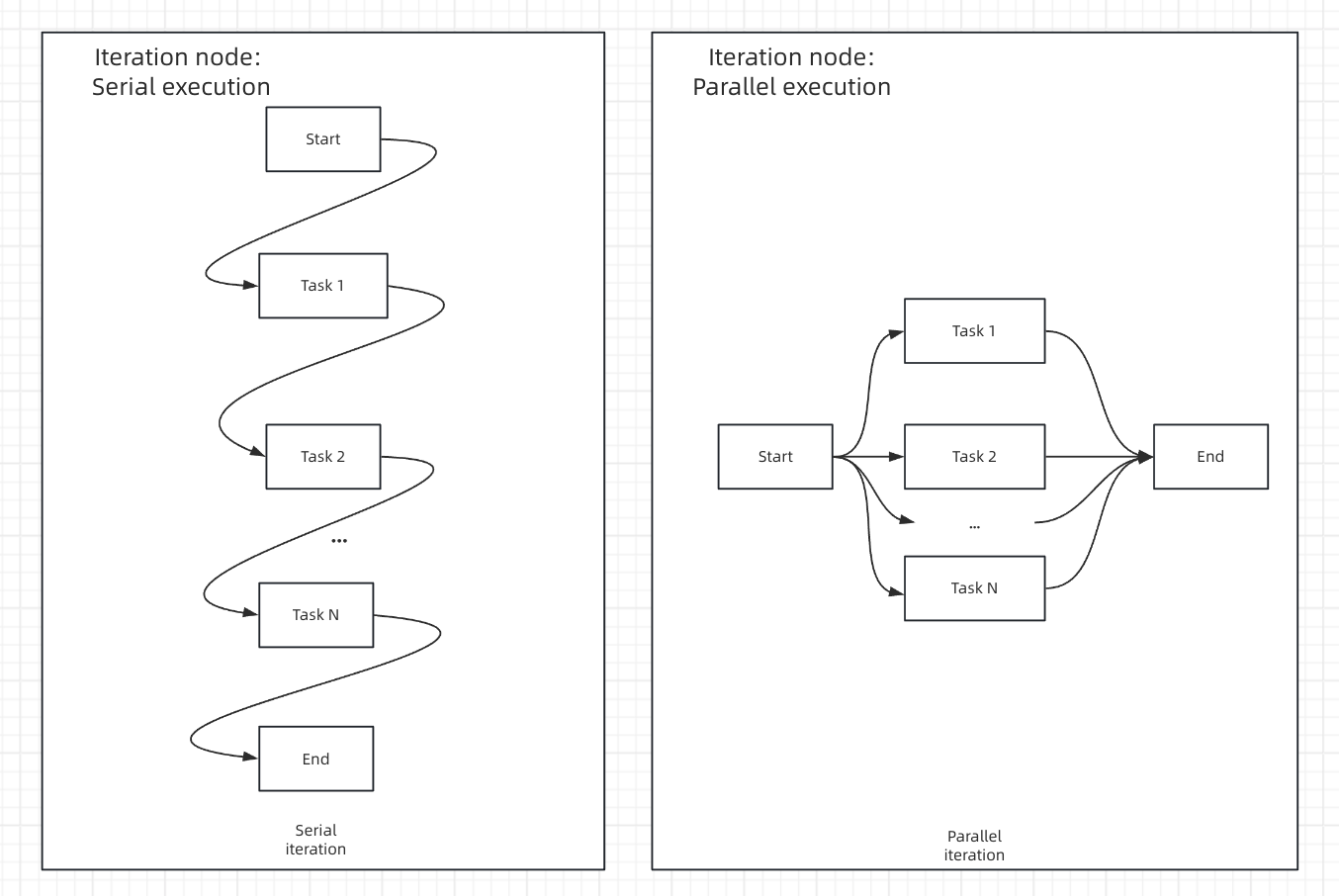
Sequential vs parallel processing comparison
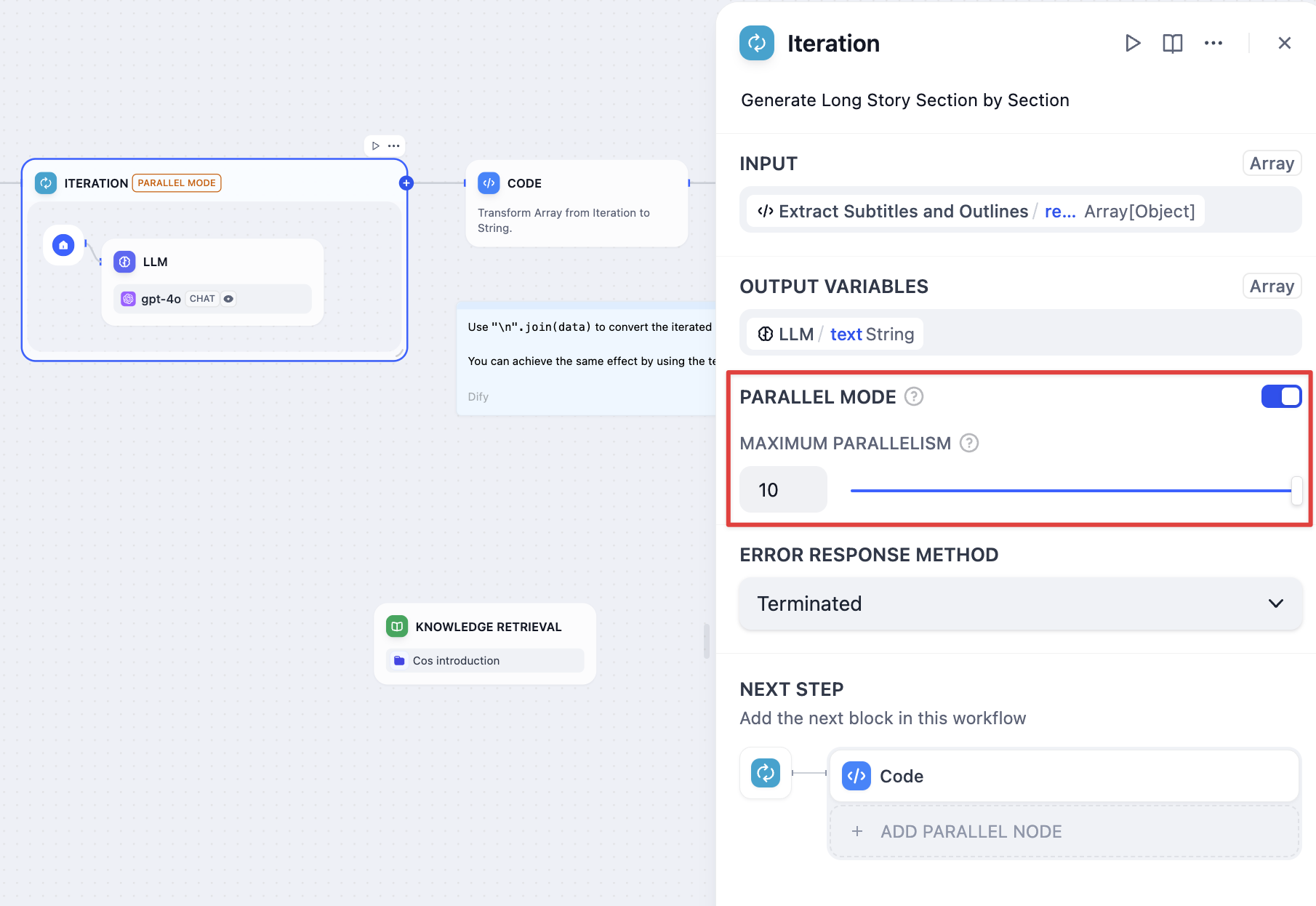
Enable parallel mode in iteration settings
Error Handling
Configure how to handle processing failures for individual array elements: Terminate - Stop processing when any error occurs and return the error message Continue on Error - Skip failed items and continue processing, outputting null for failed elements Remove Failed Results - Skip failed items and return only successful results Input-output correspondence examples:- Input:
[1, 2, 3] - Output with Continue on Error:
[result-1, null, result-3] - Output with Remove Failed:
[result-1, result-3]
Long Article Generation Example
Generate lengthy content by processing chapter outlines individually: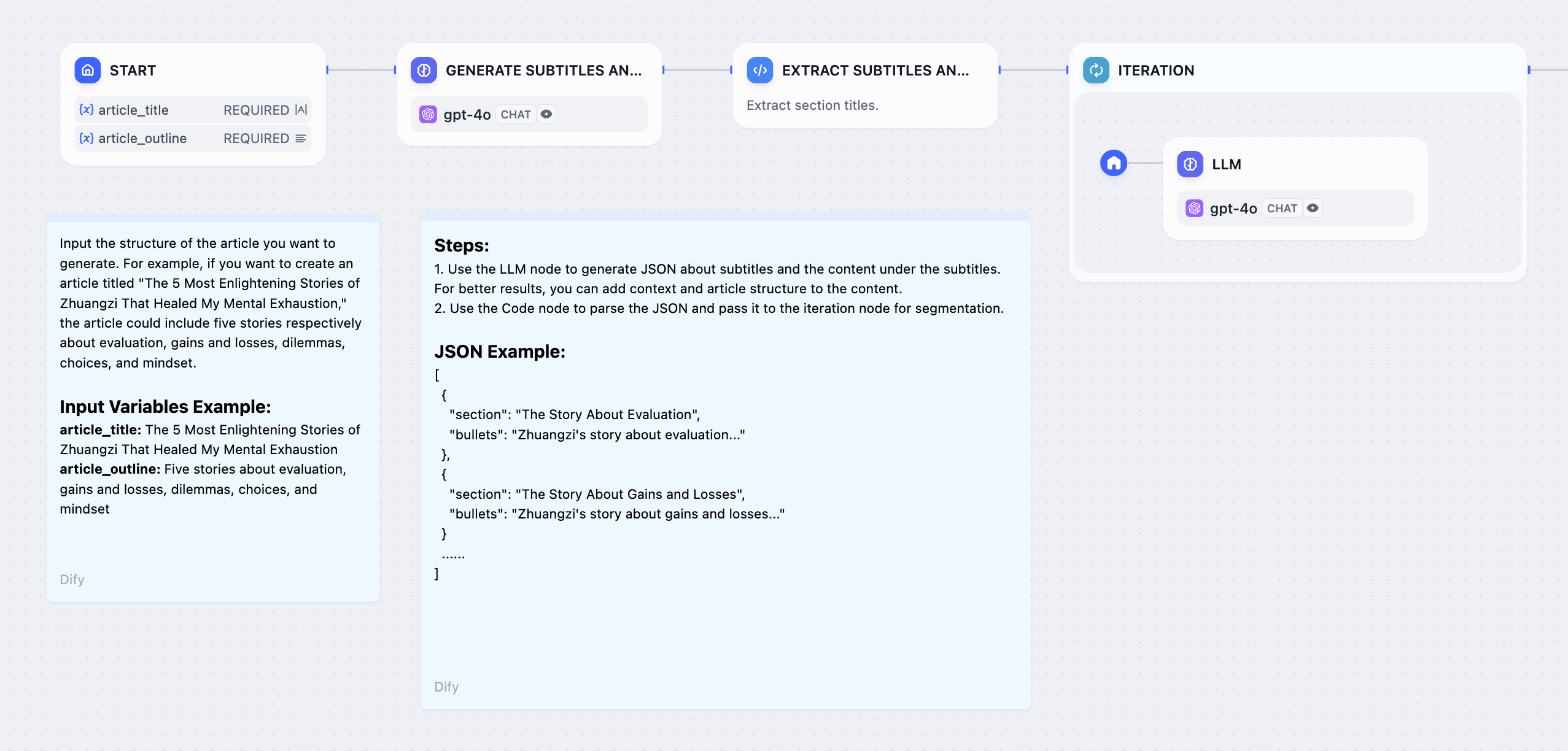
Long article generation workflow
- Start Node - User provides story title and outline
- LLM Node - Generate detailed chapter breakdown
- Parameter Extractor - Convert chapter list to structured array
- Iteration Node - Process each chapter with internal LLM
- Answer Node - Stream chapter content as it’s generated
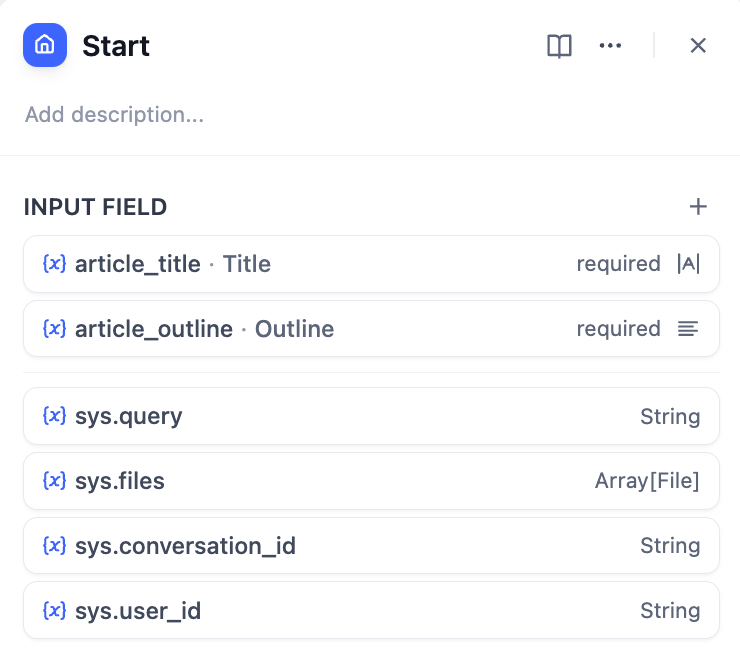
Start node configuration for story input
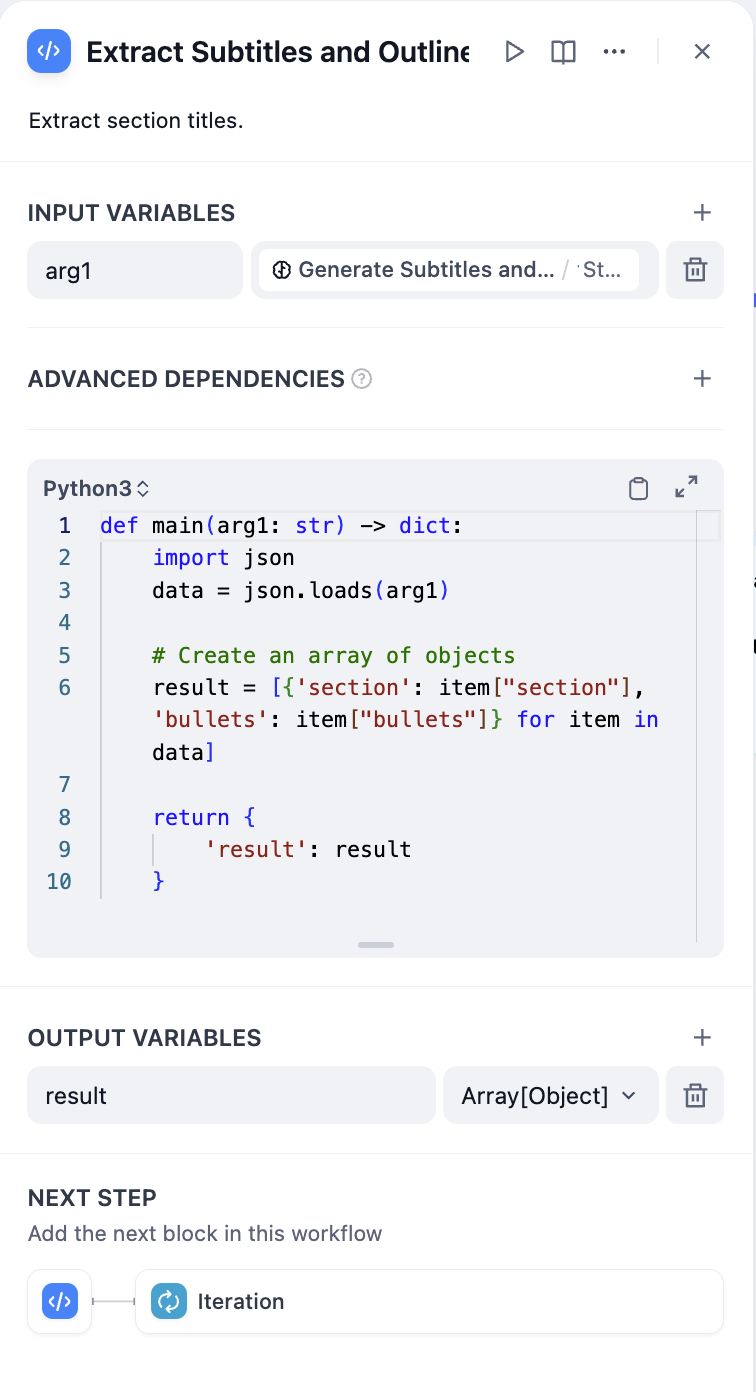
Parameter extraction for chapter structure
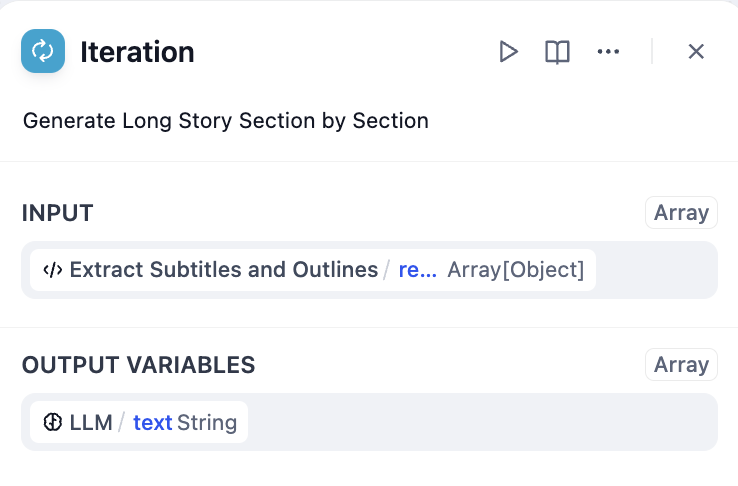
Iteration configuration with LLM processing
Parameter extraction effectiveness depends on model capabilities and instruction quality. Use stronger models and provide examples in instructions to improve results.
Output Processing
Iteration nodes output arrays that often need conversion for final use:Convert Array to Text
- Using Code Node
- Using Template Node
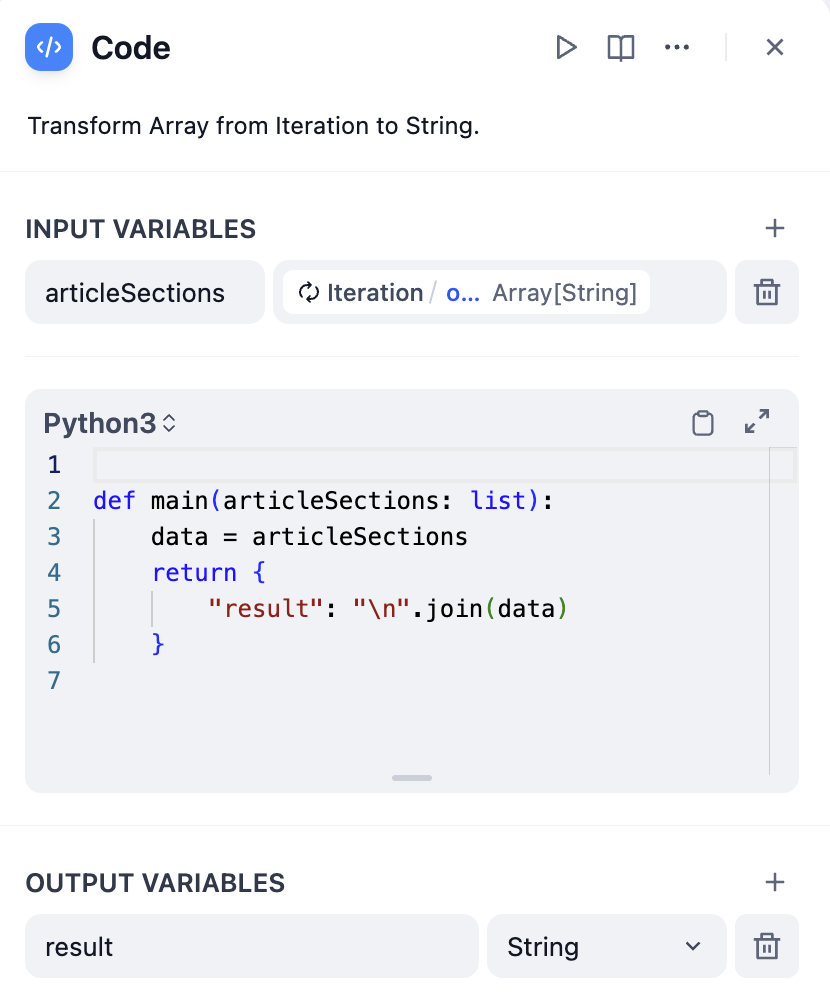
Code node array conversion