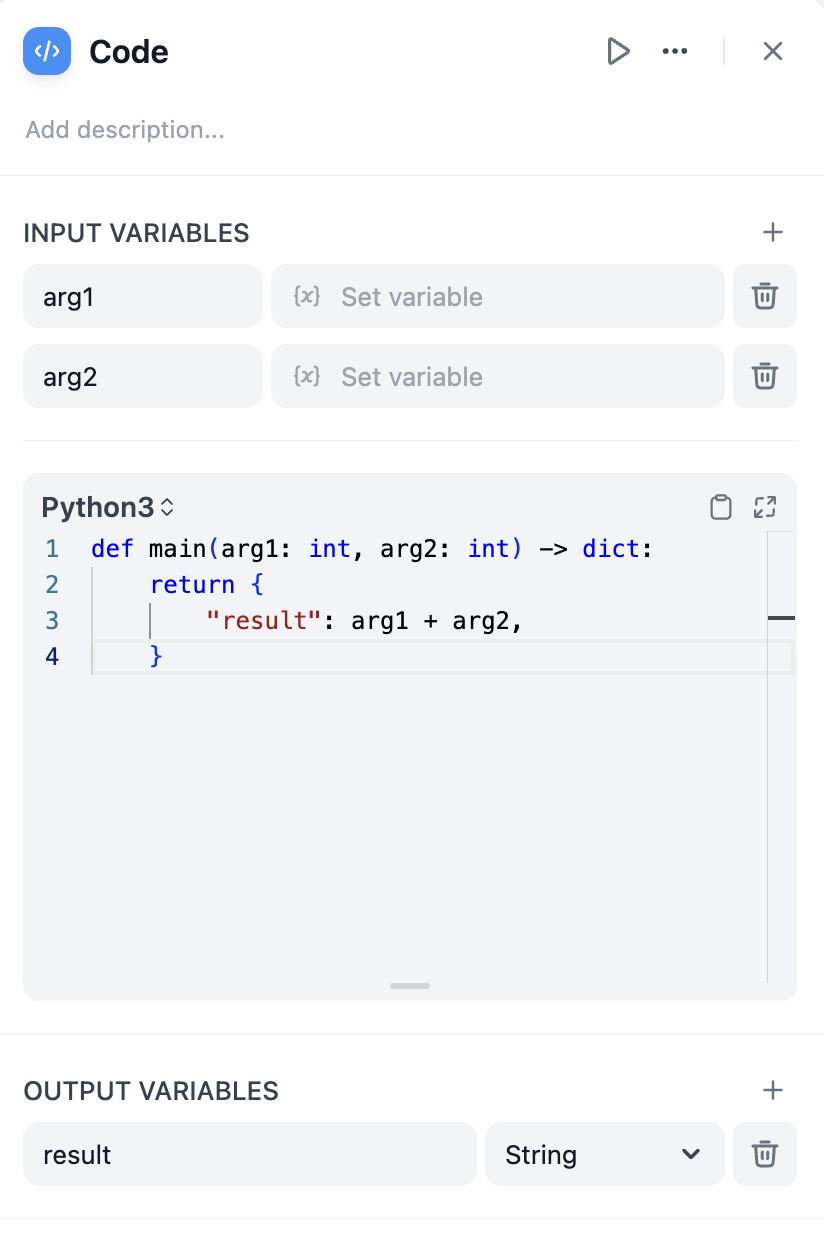
Code node configuration interface
Configuration
Define Input Variables to access data from other nodes in your workflow, then reference these variables in your code. Your function must return a dictionary containing the Output Variables you’ve declared.Language Support
Choose between Python and JavaScript based on your needs and familiarity. Both languages run in secure sandboxes with access to common libraries for data processing.- Python
- JavaScript
Python includes standard libraries like
json, math, datetime, and re. Ideal for data analysis, mathematical operations, and text processing.Error Handling and Retries
Configure automatic retry behavior for failed code executions and define fallback strategies when code encounters errors.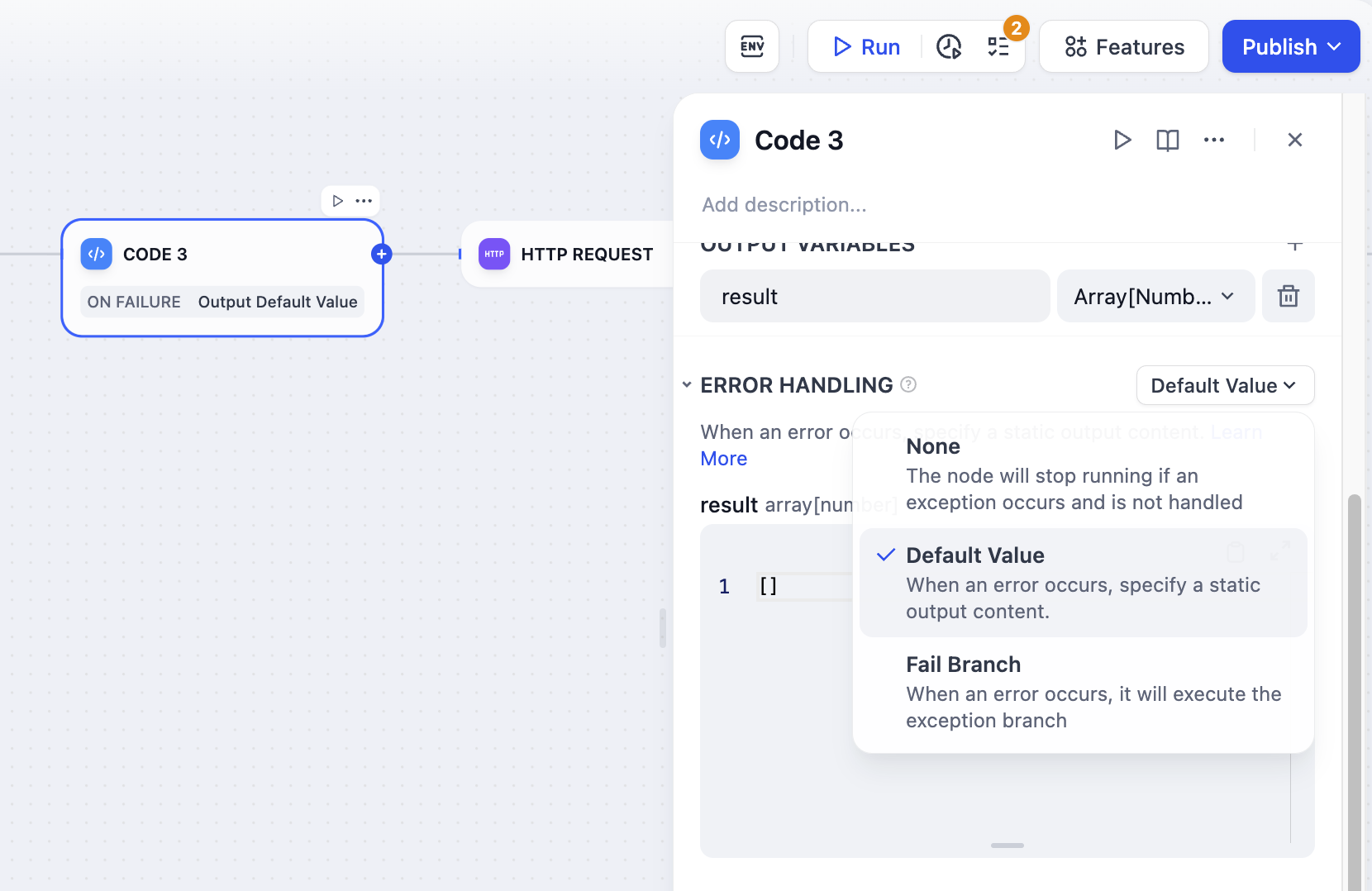
Error handling configuration options
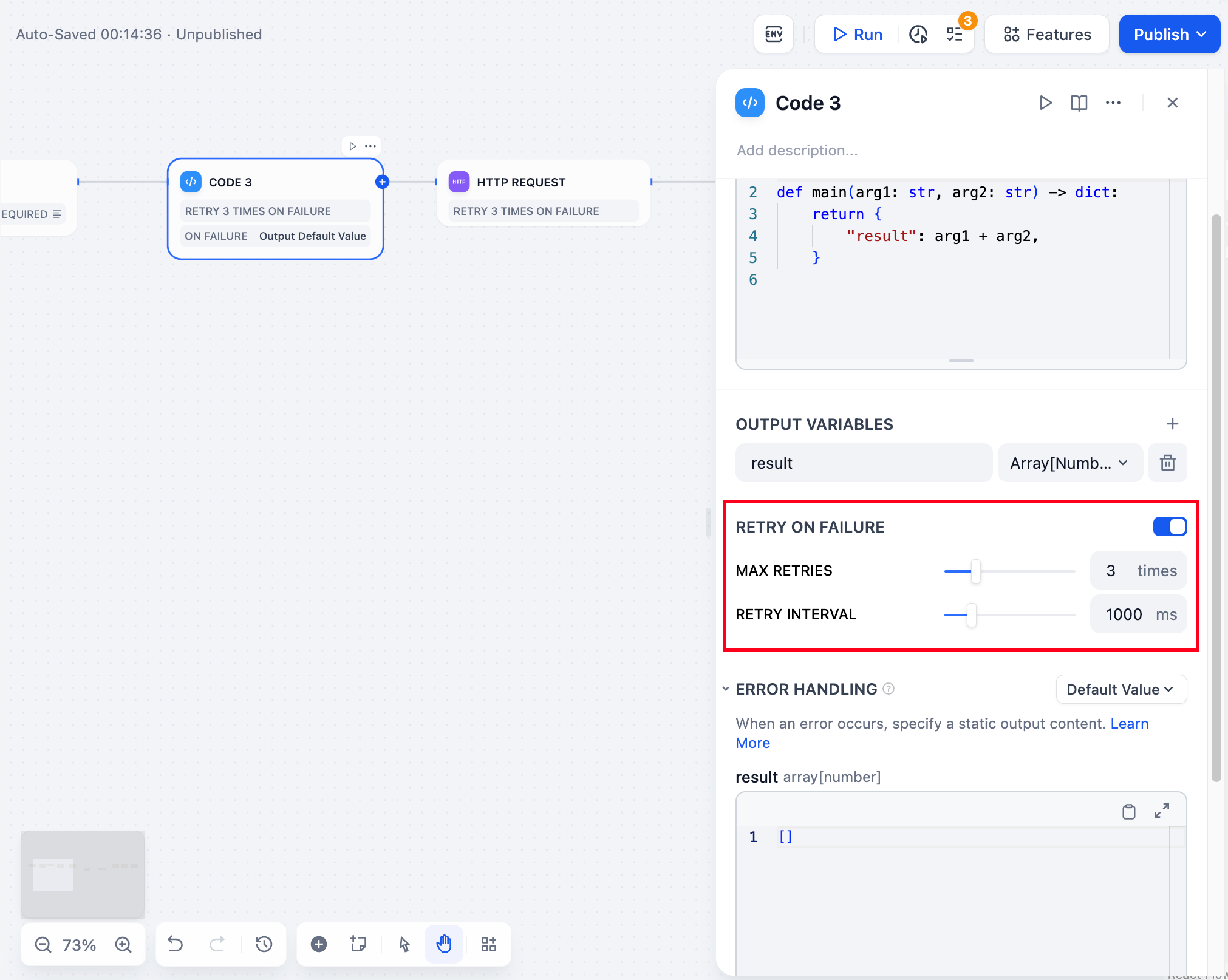
Retry configuration interface
Output Validation and Limits
Code outputs are automatically validated with strict limits:- Strings: Maximum length of 80,000 characters, null bytes are removed
- Numbers: Range from -999999999 to 999999999, floats limited to 10 decimal places
- Objects/Arrays: Maximum depth of 5 levels to prevent complex nested structures
Security Considerations
Code executes in a strict sandbox that prevents file system access, network requests, and system commands. This maintains security while providing programming flexibility. Some operations are automatically blocked for security reasons. Avoid attempting to access system files or execute potentially dangerous operations:
Security filtering by Cloudflare WAF

