The Branching Problem
Conditional workflows create parallel execution paths where only one branch runs at a time. Without aggregation, you’d need duplicate downstream nodes for each possible branch outcome, creating complex and maintenance-heavy workflows. The Variable Aggregator acts as a merge point, collecting branch outputs into a single variable that downstream nodes can reference consistently, regardless of which branch actually executed.Classification Workflow Example
When user input is classified and each category requires different knowledge retrieval, the Variable Aggregator combines the results: Without Aggregation - Complex workflow requiring duplicate LLM nodes: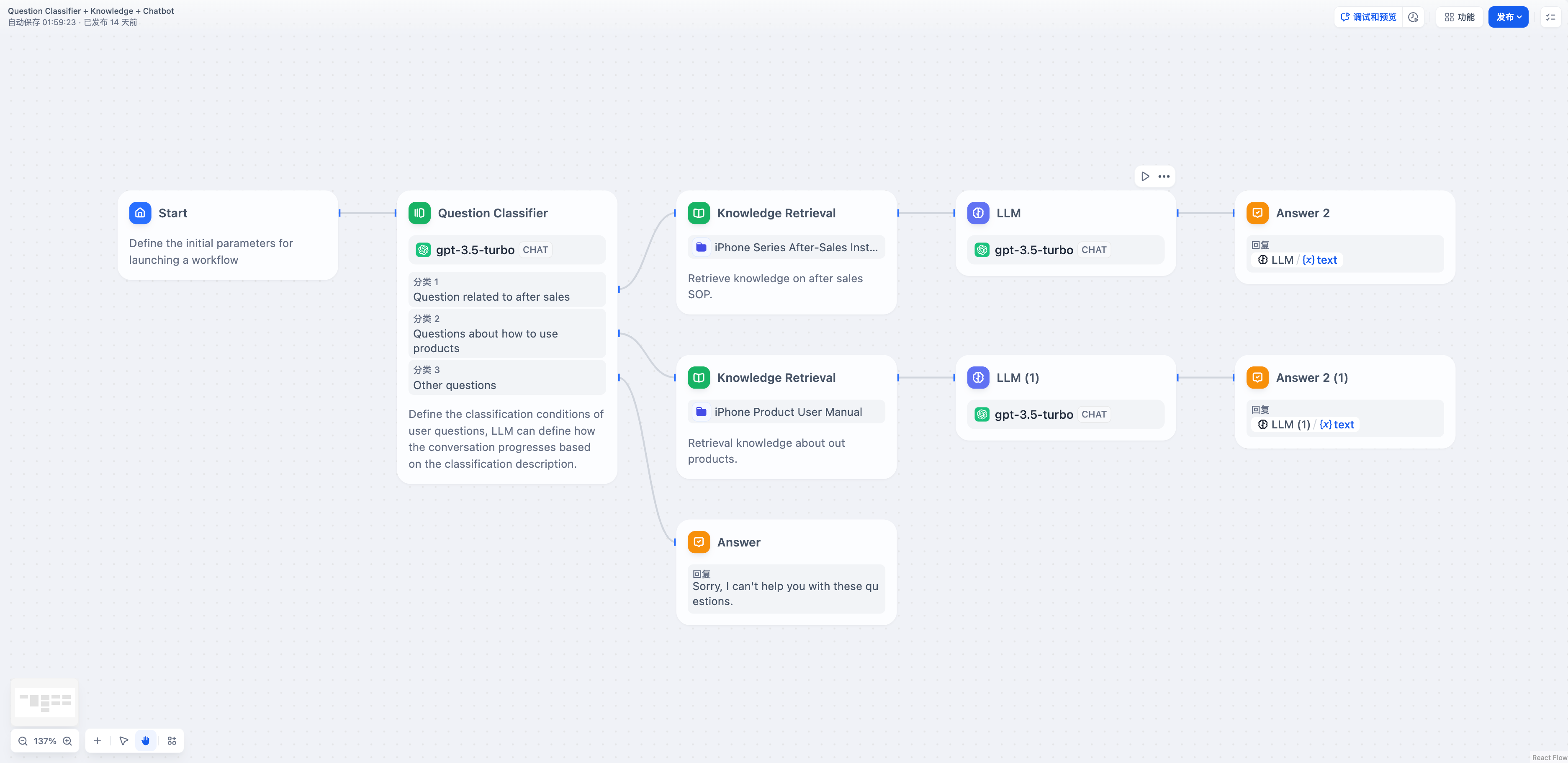
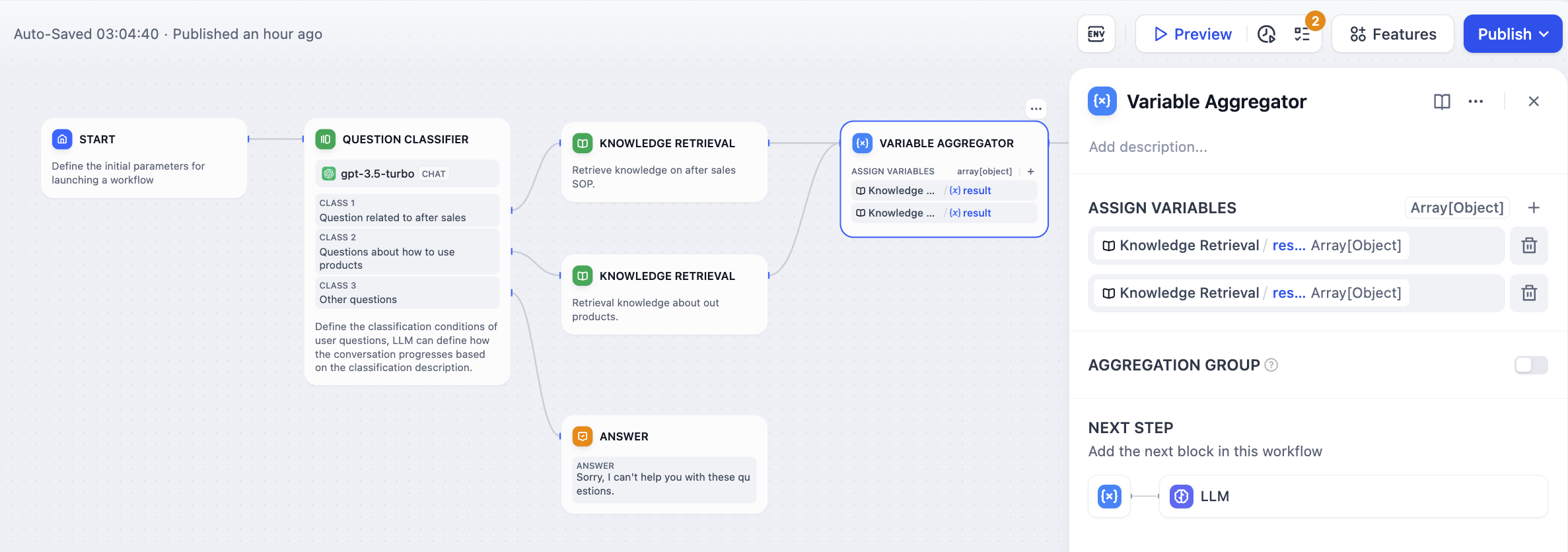
Conditional Processing Example
Similar benefits apply to If-Else branches that produce comparable outputs: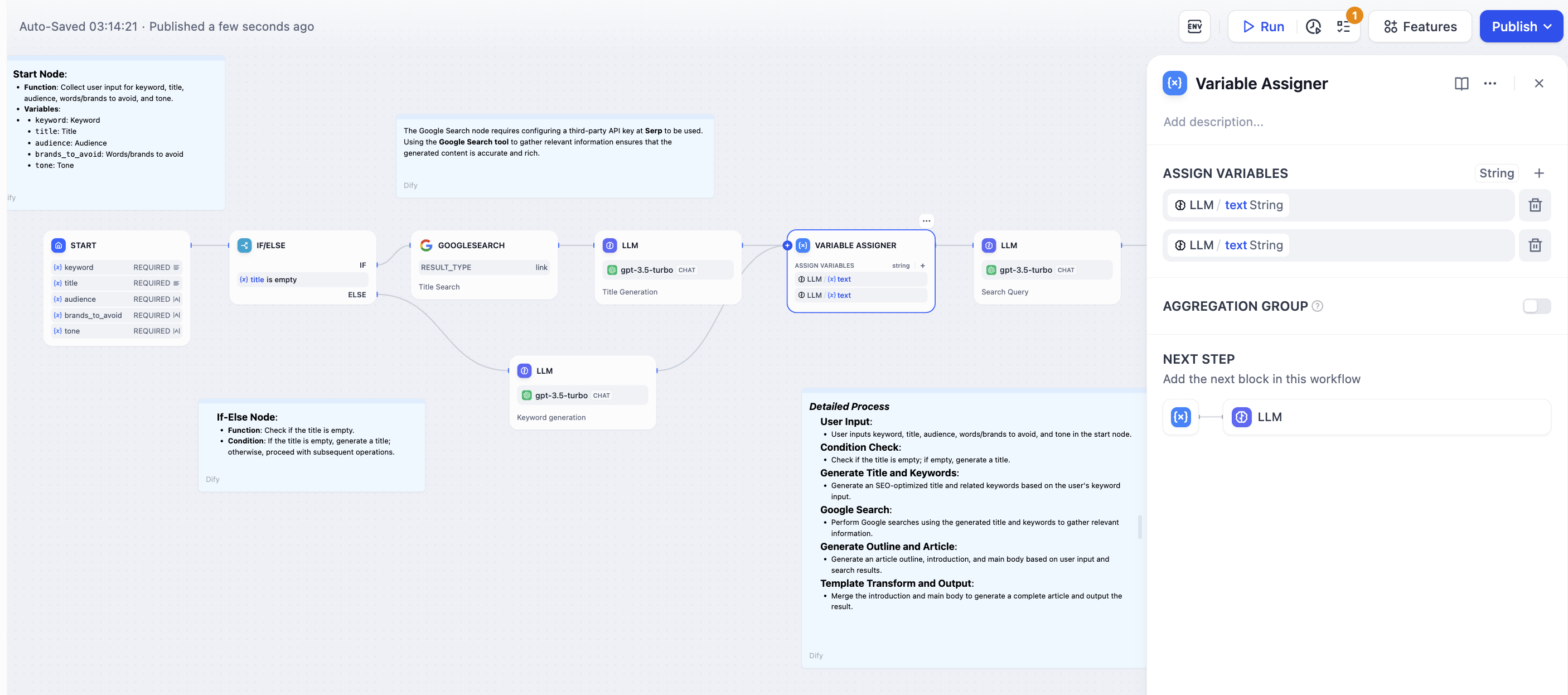
Configuration
Variable Selection
Connect variables from different workflow branches that you want to combine. Each connected variable becomes a potential input to the aggregated output.Type Constraints
Same Type Rule - All aggregated variables must be the same data type. Once you connect the first variable (e.g., String), the node only accepts variables of the same type from other branches. Supported Types:- String - Text outputs from different processing branches
- Number - Numeric calculations, scores, or measurements
- Object - Structured data objects with similar schemas
- Boolean - True/false values
- Array - Lists, collections, or multiple results

