Loop vs Iteration
Understanding when to use each repetition pattern:- Loop
- Iteration
Sequential Processing - Each cycle depends on previous resultsProgressive Refinement - Outputs improve or evolve over iterationsState Management - Variables persist and accumulate across cyclesUse Cases - Content refinement, problem solving, quality assurance
Configuration
Loop Variables
Define variables that persist across loop iterations and remain accessible after the loop completes. These variables maintain state and enable progressive workflows.Termination Conditions
Configure when the loop should stop executing: Loop Termination Condition - Expression that determines when to exit (e.g.,quality_score > 0.9)
Maximum Loop Count - Safety limit to prevent infinite loops
Exit Loop Node - Immediate termination when this node is reached
The loop terminates when either the termination condition is met, the maximum count is reached, or an Exit Loop node executes. If no conditions are specified, the loop continues until the maximum count.
Basic Loop Example
Generate random numbers until finding one less than 50: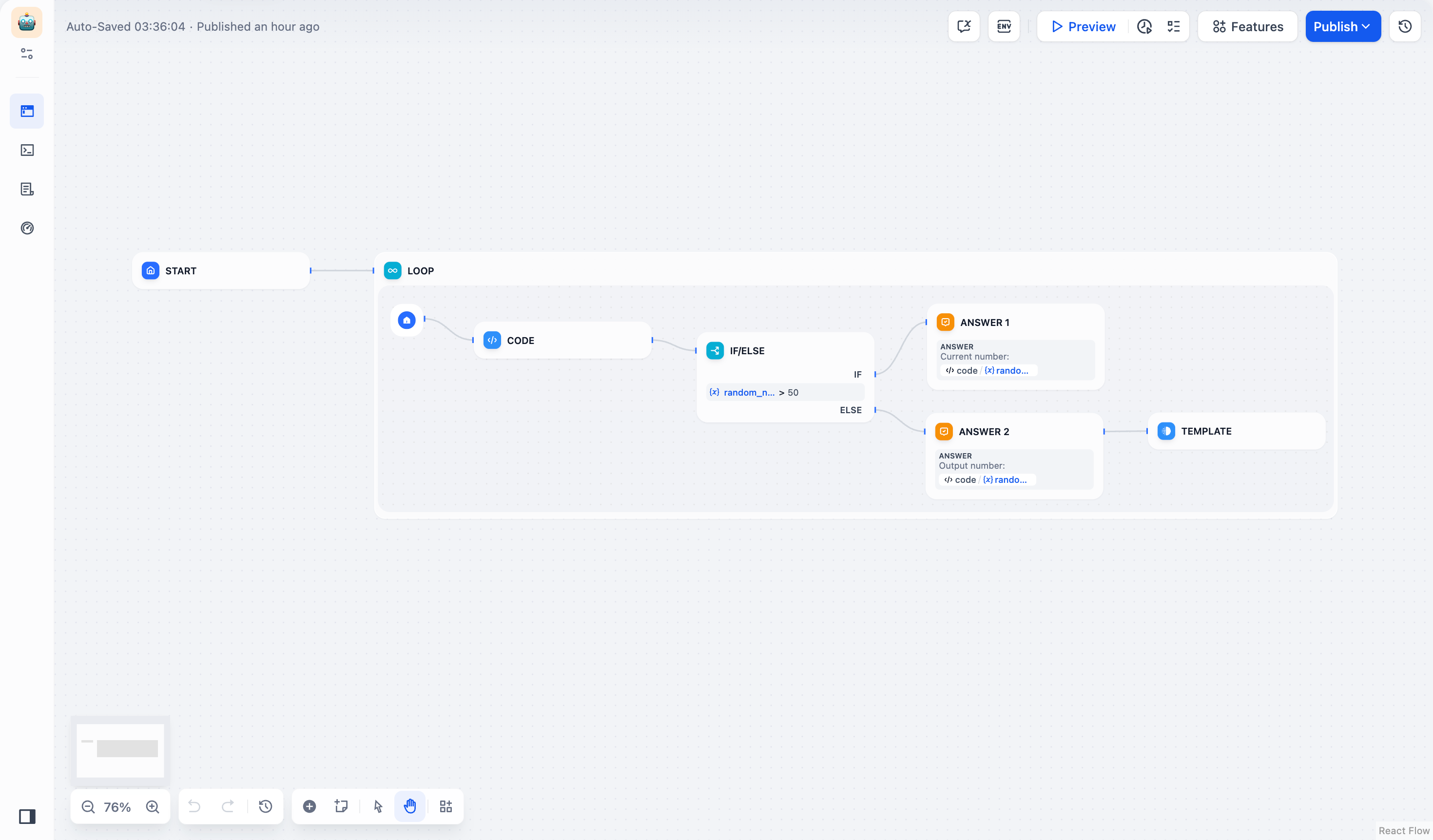
Basic loop workflow for random number generation
- Code node generates random integers between 1-100
- If-Else node checks if number is less than 50
- Template node returns “done” for numbers < 50 to trigger loop termination
- Loop continues until termination condition is met
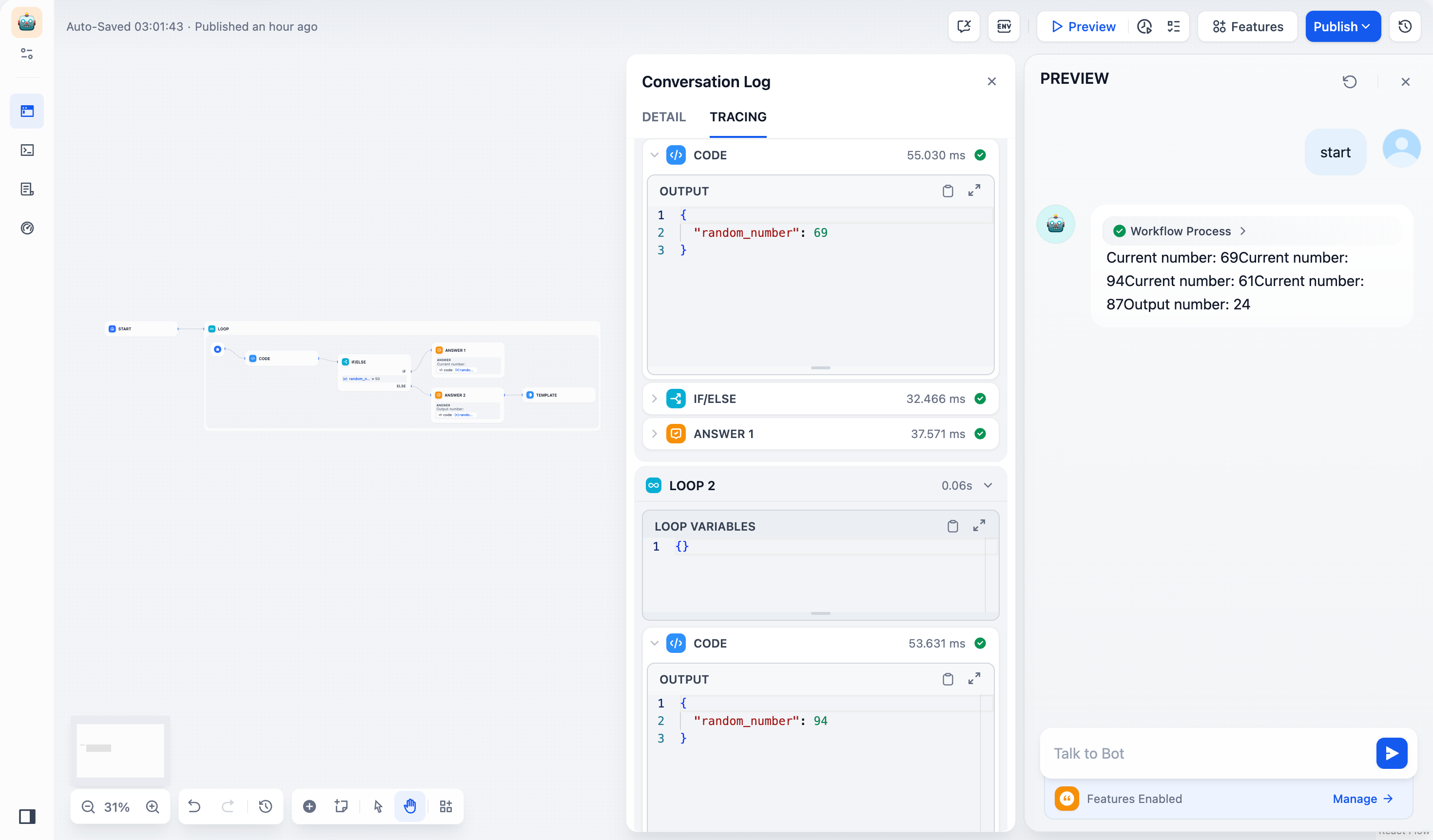
Loop execution steps and results
Advanced Loop Example
Create a poem through iterative refinement, with each version building upon the previous one: Loop Variables:num- Counter starting at 0, incrementing each iterationverse- Text variable holding the current poem version
- If-Else node checks if
num > 3to determine when to exit - LLM node generates improved poem based on previous version
- Variable Assigner updates both counter and poem content
- Exit Loop node terminates after 4 refinement cycles

